8. Troubleshooting, SSH
Linux
HOGENT toegepaste informatica
Thomas Parmentier, Andy Van Maele, Bert Van Vreckem, Jan Willem
2025-2026
Preparation
Before we begin
Set up the test environment:
- clone your Github repo for lab assignments
- on your physical system!
- open terminal in directory
troubleshooting - start the VMs
dbt- a working database serverwebt- a web server with faulty configuration
$ cd trouble-demo
$ vagrant up
[...]Introduction
Agenda
- Bottom-up approach
- Network access (Link) layer
- Internet layer
- Transport
- Application Layer
- SELinux
Interrupt me if you have remarks/questions!
Case: web + db server
Two VirtualBox VMs, set up with Vagrant
| Host | IP | Service |
|---|---|---|
webt |
192.168.76.72 | http, https (Apache) |
dbt |
192.168.76.73 | mysql (MariaDB) |
- On
webt, a PHP app runs a query on thedbt dbtis set up correctly,webtis not
Objective
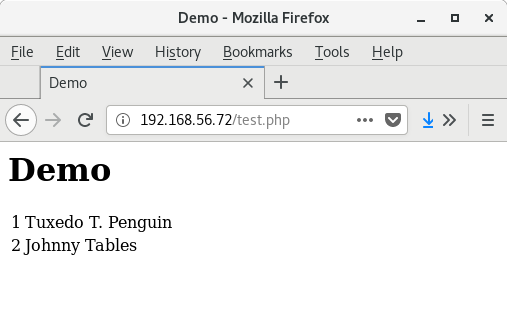
Test the database server
$ ./query_db.sh
+ mysql --host=192.168.76.73 --user=demo_user \
+: --password=ArfovWap_OwkUfeaf4 demo \
+ '--execute=SELECT * FROM demo_tbl;'
+----+-------------------+
| id | name |
+----+-------------------+
| 1 | Tuxedo T. Penguin |
| 2 | Bobby Tables |
+----+-------------------+
+ set +xShould work from
- your Linux Mint GUI VM (if it is connected to
intnetsudo apt install mysql-client - from demo VMs (
/vagrant/query_db.sh)
Use a bottom-up approach
TCP/IP protocol stack
| Layer | Protocols | Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Application | HTTP, DNS, SMB, FTP, … | |
| Transport | TCP, UDP | sockets, port numbers |
| Internet | IP, ICMP | routing, IP address |
| Network access | Ethernet | switch, MAC address |
| Physical | cables |
Network Access Layer
Network Access Layer
- bare metal:
- test the cable(s)
- check switch/NIC LEDs
- VM (e.g. VirtualBox):
- check virtual network adapter type & settings
ip link
Internet Layer
Checklist: Internet Layer
- Local network configuration
- Routing within the LAN
Know the expected values!
Checklist: Internet Layer
Checking Local network configuration:
- IP address:
ip a - Default gateway:
ip r - DNS service:
- RHEL:
/etc/resolv.conf - Fedora, Debian, etc.:
resolvectl dns
- RHEL:
Local configuration: ip address
- IP address?
- In correct subnet?
- DHCP or fixed IP?
- Check configuration (e.g.
nmcli conn showfor EL 10)
Common causes (DHCP)
- No IP
- DHCP unreachable
- DHCP won’t give an IP
- 169.254.x.x
- No DHCP offer, “link-local” address
- Unexpected subnet
- Bad config (fixed IP set?)
Watch the logs: sudo journalctl -f
Common causes (Fixed IP)
- Unexpected subnet
- Check config
- Correct IP, “network unreachable”
- Check network mask
Local configuration: ip route
- Default GW present?
- In correct subnet?
- Check network configuration
DNS server: /etc/resolv.conf
nameserveroption present?- Expected IP?
Checklist: Internet Layer
Checking routing within the LAN:
- Ping between hosts
- Ping default GW/DNS
- Query DNS (
dig,nslookup,getent)
LAN connectivity: ping
- GUI-VM-> VM:
ping 192.168.76.72 - VM -> GUI-VM:
ping 192.168.76.101 - VM -> NAT-GW:
ping 10.0.2.2 - VM -> NAT-DNS:
ping 10.0.2.3
Remark: some routers block ICMP!
LAN connectivity: DNS
dig icanhazip.comnslookup icanhazip.comgetent ahosts icanhazip.com
LAN connectivity
Next step: routing beyond GW
Transport Layer
Checklist: Transport Layer
- Service running?
sudo systemctl status SERVICE - Correct port/inteface?
sudo ss -tulpn - Firewall settings:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
Is the service running?
systemctl status httpd.service
active (running)vs.inactive (dead)systemctl start httpd- Fail? See below (Application layer)
- Start at boot:
enabledvs.disabledsystemctl enable httpd
Firewall settings
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
- Is the service or port listed?
- Use
--add-serviceif possible- Supported:
--get-services
- Supported:
- Don’t use both
--add-serviceand--add-port - Add
--permanent --reloadfirewall rules
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=https --permanent
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reloadCorrect ports/interfaces?
- Use
ss(notnetstat)- TCP service:
sudo ss -tlnp - UDP service:
sudo ss -ulnp
- TCP service:
- Correct port number?
- See
/etc/services
- See
- Correct interface?
- Only loopback?
Application Layer
Checklist: Application Layer
- Check the logs:
journalctl - Validate config file syntax
- Use (command line) client tools
- e.g.
curl,smbclient(Samba),dig(DNS), etc. - Netcat (
ncat,nc)
- e.g.
- Other checks are application dependent
- Read the reference manuals!
Check the log files
- Either
journalctl:journalctl -f -u httpd.service - Or
/var/log/:tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log
Check config file syntax
- Application dependent, for Apache:
apachectl configtest
Read the fine manual!
- RedHat
Manuals:
- System Administrator’s Guide
- Networking guide
- SELinux guide
- Reference manuals, e.g.:
- Man pages
- smb.conf(5), dhcpd.conf(5), named.conf(5), …
What about ChatGPT?
- LLMs will hallucinate
- Advice may be outdated
- Advice may be irrelevant
When you manage production systems, nothing beats the quality of official documentation and manuals!
SELinux troubleshooting
SELinux
- SELinux is Mandatory Access Control in the Linux kernel
- Settings:
- Booleans:
getsebool,setsebool - Contexts, labels:
ls -Z,chcon,restorecon - Policy modules:
sepolicy
- Booleans:
Check file context
- Is the file context as expected?
ls -Z /var/www/html
- Set file context to default value
sudo restorecon -R /var/www/
- Set file context to specified value
sudo chcon -t httpd_sys_content_t test.php
Check booleans
getsebool -a | grep http
- Know the relevant booleans! (RedHat manuals)
- Enable boolean:
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db on
General guidelines
Back up config files before changing
Be systematic, bottom-up
Be thorough, don’t skip steps
Do not assume: test
Know your environment
Know your log files

Read The F*** Error Message!
Open logs in separate terminal
Small steps
Validate the syntax of config files
Reload service after config change
Verify each change
Keep a cheat sheet/checklist
Use a configuration management system
Automate tests
E.g. https://github.com/HoGentTIN/elnx-sme/blob/master/test/pu001/lamp.bats
Don’t ping Google!
Why?